GitHub Introduction
5 minute read
GitHub in GEN242
- Note, this class will make heavy use of GitHub
- Homework assignments will be submitted and graded on GitHub Classroom
- Course projects will also use private GitHub repositories: one repository for each course project (shared among students of each project)
- Each student will need a personal GitHub account. They can be created here.
- GitHub provides an unlimited number of free public repositories to each user. Via GitHub Education students can sign up for an extended number of free private GitHub accounts (see here).
- For beginners this quick guide may be useful
What are Git and GitHub?
- Git is a version control system similar to SVN
- GitHub is an online social coding service based on Git
- Combined Git/GitHub: environment for version control and social coding
Installing Git
- Install on Windows, OS X and Linux
- When using it from RStudio, it needs to find the Git executable
Git Basics from Command-Line
Also try interactive git tutorial.
-
Finding help from command-line
git <command> --help -
Initialize a directory as a Git repository (here
my_repos).mkdir my_dir; cd my_repos git init -
Add specific files to Git repository (staging area)
touch myfile git add myfile -
Add all files recursively
To ignore specific files (e.g. temp files), list them in a
.gitignorefile in your repository’s root directory. Regular expressions are supported. See here for more details.git add -A :/ -
After editing file(s) in your repos, record a snapshot of the staging area
git commit -am "some edits"
GitHub Basics from Command-Line
-
Generate a new remote repository on GitHub online with same name as in previous section (or use hub or GitHub CLI command-line wrappers for this). To avoid errors with the online method, do not initialize the new repository with README, license, or
.gitignorefiles. You can add these files after your project has been pushed to GitHub.git remote add origin git@github.com:<user_name>/<repos_name>.git # Use here my_repos under <repos_name>, if example from previous section is used. -
Push updates to remote. Next time one can just use
git pushgit push -
Clone existing remote repository
git clone git@github.com:<user_name>/<repos_name>.git -
Before working on project, update local git repos
git pull -
Make changes and recommit local to remote
git commit -am "some edits"; git push
Important When Working with Private GitHub Repositories!
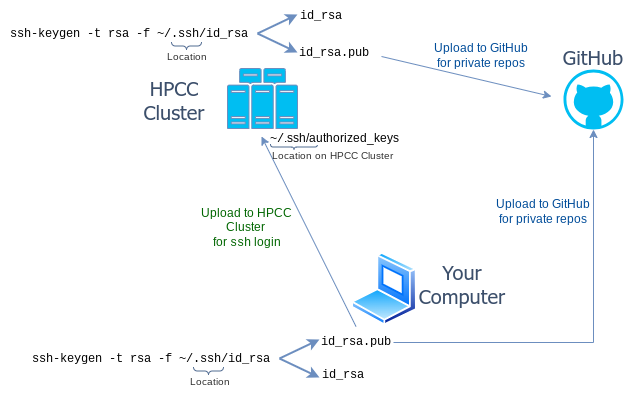
In order to work with private GitHub repositories, like the ones used in GEN242, users need to activate in their GitHub account under Settings as authentication method an SSH Key.
The latter SSH Key method is usually preferred. To push to a private GitHub repository from the HPCC cluster, you need to generate an SSH Key from your home account on the HPCC cluster using
the standard Linux ssh-keygen method as described here, and then upload the
newly generated public SSH Key of your HPCC account located under ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to GitHub. The same method can be used to
create an SSH Key on a personal computer and then upload the public key to GitHub. Usually, one should create a dedicated key
pair for each computer one uses and upload the corresponding public keys to GitHub. If you are new to SSH Keys, then please read this short introduction.
Exercise
Run the following git/github excercise from the command-line. Do this after creating a GitHub repos according to the instructions above or online as outlined here.
git clone git@github.com:<user or org>/<repo name>
cd <repo name>
git pull
touch test # Creates empty file for testing
git add test # or use '-A' for all
git commit -am "some edits"
git push
##-> Edit test file online and then run `git pull` to inspect changes
Online file upload
Useful for new users who want to upload their homework assignments to GitHub but are not familiar enough with the command-line yet.
- Press
Add filebutton on your repository, and thenUpload files. - Under the file path window add required subdirectory structure and a dummy file name (e.g.
Homework/HW1/dummy.txt) - After this press
Upload filesand upload any file (e.g. homework) to the newly create directory. After this the initial dummy file can be deleted. The latter is necessary since empty directories are not visible on GitHub.
Using GitHub from RStudio
Note: one can also set up SSH Keys from RStudio. How to do this is explained here.
-
After installing Git (see here), set path to Git executable in Rstudio:
- Tools
>Global Options>Git/SVN
- Tools
-
If needed, log in to GitHub account and create repository. Use option
Initialize this repository with a README. -
Clone repository by copying & pasting URL from repository into RStudio’s ‘Clone Git Repository’ window:
- File
>New Project>Version Control>Git>Provide URL
- File
-
Now do some work (e.g. add an R script), commit and push changes as follows:
- Tools
>Version Control>Commit
- Tools
-
Check files in staging area and press
Commit Button -
To commit changes to GitHub, press
Push Button -
Shortcuts to automate above routines are here
-
To resolve password issues, follow instructions here.
Viewing static HTML files on GitHub
Simple viewing of HTML files on GitHub can be enabled by making the following changes to a public repos. Without these adjustments, one needs to download an HTML file from GitHub in order to view the rendered content. An example GitHub repos for showcasing this feature is here.
- Make sure your GitHub repos is public
- Go to
Settings - Select
Pagesin menu on left - Select
Deploy from a branchunderSource - Select a branch in the
GitHub Pagessection - Save the changes and wait until a URL is provided for your site.
- To test, upload an HTML file and append its paths to the URL provided in previous step.